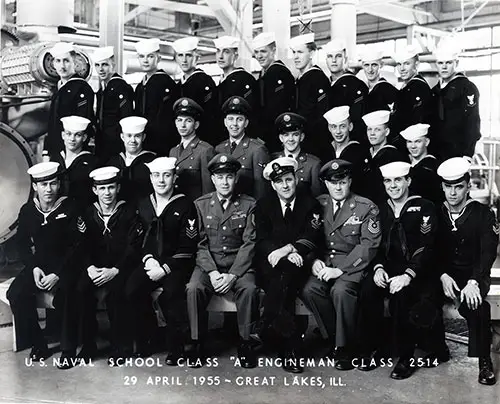
NTC Great Lakes 1955 Company 2514 Group Photo
Group Photograph: U.S. Naval School Class "A" Engineman, Class 2514, 29 April 1955, Great Lakes Naval Training Center. GGA Image ID # 113927a113. Click to View Larger Image.
Engineman (EN)
The internal-combustion engine, either diesel or gasoline, plays a tremendously important role in powering the ships and small craft of the Navy. These engines must be properly maintained, repaired, and operated. The most important work of the Navy Engineman centers around these jobs.
DUTIES AND RESPONSIBILITIES
Enginemen operate, maintain, and repair internal-combustion engines. Most Enginemen are engaged in these tasks in diesel-driven ships and craft, but some work with high-powered gasoline engines such as those used in motor torpedo boats and other small craft. Enginemen also operate and maintain auxiliary engines and the refrigeration and air-conditioning equipment on diesel-driven ships.
Examples of jobs performed—
- Operation: Operate main engines and auxiliary engineroom machinery, including starting and stopping of diesel and gasoline engines.
- Maintenance and Repair: Maintain and lubricate diesel and gasoline engines and equipment, and various accessories. Perform routine maintenance and repair work on main propulsion and auxiliary engines. Make major overhaul and repairs by disassembly, replacement, and reassembly according to Navy standards.
- Tests and Inspections: Conduct routine tests and inspections of such parts as air compressors, governors, and fuel and lubricating oil purifiers.
- Refrigeration: Operate and make repairs to refrigeration and air-conditioning systems on vessels propelled by internal-combusion engines.
- Tools: Perform simple operations on lathes, drill presses, milling machines, and shapers. Cut threads in pipe, make joints in pipelines, remove and replace insulation, and solder joints.
- Instruments: Use measuring instruments needed in engine overhaul such as micrometers, bridge gages, and inside and outside calipers. Read accurately such instruments as thermometers, pressure gages, and pressure indicators.
Examples of skills and knowledge acquired:
- Construction, operation, and maintenance of diesel and gasoline engines.
- Functions and interrelationships of the main propulsion systems (direct drive and gear drivel {towered by diesel and gasoline engines.
- Function of compressors, centrifugal pumps, condensers, and evaporators in a refrigerating system.
- Operation of the various types of valves utilized in main propulsion and auxiliary equipment including gate, globe, check, needle, pilot, butterfly, and solenoid types.
- Basic principles governing operation of governors, hydraulic couplings, and reduction gears.
- Basic principles of refrigeration, types of refrigerants, and tests for leaks.
- Basic principles of air conditioning.
- Principles of simple mathematics including common fractions, decimals, percentages, and ratios.
- Operation of generators, electric motors, ignition systems, and other electrical devices associated with diesel or gasoline engines.
- Blueprint reading and the sketching of machine parts.
- Electricity as applied to motors, generator regulators. and generators on internal-combustion engines.
- Use of measuring instruments such as micrometers. bridge gages, and inside and outside calipers, which are used in engine overhaul.
Enginemen in the lower pay grades generally perform the more routine duties; men in the higher pay grades perform the more responsible duties and instruct and supervise others.
PLACE OF WORK
Enginemen may be assigned to any ship, to any naval shipyard, or to any repair facility afloat or ashore. It is the basic policy of the Navy to rotate its personnel between sea or advanced base assignments and assignments within continental limits of the United States.

Engineman Making Records. US Navy Vocational Information Briefs. GGA Image ID # 1ffae56212
QUALIFICATIONS AND PREPARATION
Personnel should be average or above in general learning ability and ability to use numbers. In addition, they should have a liking for engines and things mechanical.
A background in shop courses and in practical and shop mathematics is desirable. Courses in algebra, geometry, and physics would be helpful. Experience in automotive repair is invaluable.
TRAINING PROVIDED
Upon entering the Navy all personnel are sent to a Recruit Training Command for 9 weeks of indoctrination and basic training, guidance, and classification. Upon completion of this period, training for the rating of Engineman may be obtained through service schools or through the accumulation of experience on the job and the study of manuals provided for the purpose. The curriculum of the U. S. Naval School, Enginemen, provides for study and work experience in the following areas:
- Mathematics, blueprint reading, metals and their properties, temperature and pressure instruments, and basic electricity.
- Threadcutting, pipefitting, soldering, and use of hand tools.
- Theory, construction, and operation of diesel and gasoline engines and their associated equipment such as governors, motors, generators, valves, gears, blowers, and fuel injectors.
- Auxiliaries, including boilers, distilling plants, air compressors, pumps, refrigeration, and air conditioning.
- Organization and damage control.
Advanced schooling is available to certain petty officers in this rating in order that they may develop additional technical skills.
PATH OF ADVANCEMENT
- Seaman Recruit or Fireman Recruit
- Fireman Apprentice
- Fireman
- Engineman, Third Class
- Engineman, Second Class
- Engineman, First Class
- Chief Engineman
- Warrant Officer
- Commissioned Warrant Officer
- Commissioned Officer
RELATED NAVAL OCCUPATIONS
- Machinist’s Mate (MM)
- Machinery Repairman (MR)
- Boilerman (BT)
- Pipe Fitter (FP)
RELATED CIVILIAN JOBS
Training and experience in the Navy provide personnel with the background, skills, and knowledge for many civilian occupations. The extent to which personnel will be prepared or qualified for these occupations will depend largely on the breadth of their' Navy experience and the degree of advancement they have achieved, as well as upon occupational or apprenticeship credit granted by civilian authority. Those who make the Navy their career find they are generally well qualified for high-paying, supervisory, civilian jobs on retirement.
Some civilian jobs closely related to those performed by Enginemen are listed below:
- Diesel Engine Operator, Stationary
- Diesel Mechanic
- Ignition Repairman II
- Ignition and Carburetor Mechanic
- Gas Engine Mechanic
- Foreman, Garage Mechanics
- Engineer V
- Dynamometer Tester Motor I
EMERGENCY SERVICE RATINGS
In time of national emergency this occupation will be subdivided into the following emergency service occupations:
- Engineman D (Diesel Engineman) (END)
- Engineman G (Gasoline Engineman) (ENG)
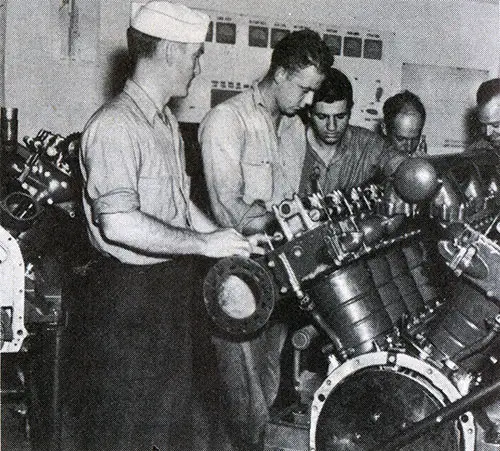
Enginaman Studying a PT Boat Gasoline Engine. US Navy Vocational Information Briefs. GGA Image ID # 1ffb28de22

